计算机图形学知识综述
CG 复习总结 Computer Graphics
Goals in Detail
- Introduce basic concepts of computer graphics
- Describe the 3D graphic representation flow in current PC
- Describe some fundamental algorithms used in computer graphics
- Introduce the computer graphics programming with OpenGL
- Enhance the ability on programming and data structure exertion
- Research in CG community
Contents
- Survey of CG and Overview of Graphics Systems
- Line/Circle Drawing algorithm
- Polygon Fill Algorithm
- Introduction to OpengGL Programming
- Lighting model
- Geometric Transformations
- Clipping
- Visible-Surface Detection
Graphics in “Computer Graphics”
是指由点、线、面、体等几何要素 (geometric attribute) 和明暗、灰度(亮度)、色彩等视觉要素 (visual attribute) 构成的,从现实世界中抽象出来的图或形
Tasks of CG
Generating 2D images of a 3D world represented in Computer by Computing, NOT by sensing.
(3D Models -> rendering -> 2D images)
Overview of the course
Geometry (Modeling)
- View, Transformation of Models (模型的投影和变换)
- Bezier Curves
- B-Spline Curves
- Triangle Mesh(三角网)
- Deformation (变形)
Rendering : photorealistic rendering and non-photorealistic rendering
- Basic Concepts, OpenGL
- Lighting (光照)
- Ray Tracing (光线跟踪)
- Acceleration of Ray Tracing(光线跟踪加速)
- Texture (纹理)
- Shadow (阴影)
- Radiosity(辐射度)
Research Hot Topics
- Rendering
- Computer Animation
- Geometry
- Video-based rendering
Geometric Transformation
- Geometric transformation in 3D space
- Translation(平移)
- Scaling(放缩)
- Rotation(旋转)
- Homogeneous Coordinates(齐次坐标)
- Global Transformation and Local Transformation
Projection
Perspective projection (透视投影)
Perspective projections in OpenGL
void glFrustum(GLdouble left, GLdouble right, GLdouble bottom, GLdouble top, GLdouble znear, GLdouble zfar);
void gluPerspective(GLdouble fovy, GLdouble aspect, GLdouble zNear, GLdouble zFar);Parallel projection (平行投影)
Clipping
Point clipping (点的裁减) :是否在区域内部
Line clipping (线的裁减)
Binary Region Codes(区域编码) :4-digit code CtCbCrCl(上下右左)
Mid-point Partition Algorithm(中点分割算法:二分)
Polygon clipping (多边形的裁减)
Transformation from window to viewport
glFrustum 函数和 glViewport 函数
Graphics Pipeline
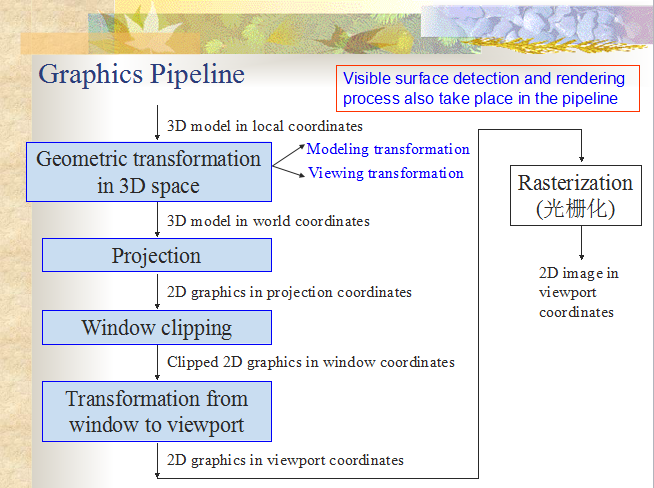
图形学流水线可以概括为:
局部坐标的 3D 模型通过 3D 空间的几何转换得到全局坐标的 3D 模型,通过投影得到投影坐标系中的 2D 图形,通过窗口裁剪得到窗口坐标系中已裁剪的 2D 图形,通过窗口到视口的变换,得到视口坐标系中的 2D 图形,通过光栅化得到视口坐标系中的 2D 图像
Visibility Detection
Why to do it
- Avoiding ambiguity (消除二义性)
- Get the correct visual effect (正确绘制)
- Improving rendering rates (提高绘制效率)
Back-Face Detection(后向面判别)
实现与平面法向的夹角 V· N<0 为前向面,V· N>0 为后向面
Visible-Surface Detection Methods
- Ray Casting Method(了解):光线投射法
- Z-buffer, Scan-Line Z-buffer(详细掌握)
- stores a depth value for each pixel on the screen
- Scan-Line Z-buffer:To process one scan-line of the screen at a time in order to reduce storage requirements
- Area-Subdivision Method(了解)
- Depth Sorting Method(整体掌握)
Lighting
Shading(着色)
Polygonal Shading
- Flat shading(平面着色)
- Interpolative shading(插值着色):Interpolate color in interior
- Gouraud shading(高洛德着色 )
- Face normal 取平均得到 vertex normal 计算得到 vertex color 然后 Interpolate colors across polygon
- Phong shading (different from Phong illumination)(Phong 着色)
- Interpolate normals rather than colors
Photorealistic Rendering Ray-tracing
- Introduction of ray tracing
- Ray intersection(光线求交)
- shadows(阴影)
- Transparence and specular reflection(透明和镜面反射)
- textures(纹理)
光线追踪的核心在于光线求交(Ray intersection)
The Simplest Ray Tracing:Ray Casting(光线投射)
Texture
Texture mapping(纹理映射) or texturing(贴纹理)
Texture usage
- Texture acquisition(纹理获取)
- Taking photograph
- Procedure texture(过程纹理)
- Texture synthesis(纹理合成)
- Texture mapping(贴纹理)
- Texture filtering(纹理滤波)
- Aliasing(走样) 和 Anti-aliasing(反走样)
NPR stroke(非真实感绘制过程)
Let computer have partial or aggressively complete capability of artists, that is selectively rendering objects stylized and abstracted.(让计算机有艺术家的能力:抽象)
名词解释
- Animation :动画
- Simulation :模拟,仿真
- Deformation :变形
- Triangle Mesh :三角网
- 3D Data Acquisition and Modeling :三维数据采集和建模
- Color Space :RGB、CMY、HSV、CIE XYZ
- Diffuse :漫发射
- Ambient :环境光
- Specular :高光(镜面反射)
- Cathode ray tube(CRT) :阴极射线管
- Raster-Scan Display :光栅扫描显示器
- frame buffer :帧缓冲(A memory area that image is stored in)
- Resolution :分辨率
- OpenGL :Open Graphic Library (开放的图形编程库)
- Clipping :剪裁
- Composite Transformation :综合变换
- Depth overlaps checking :深度重叠测试
Details
- 画出多个茶壶围绕中心一周
- void glTranslatef(float x, float y, float z); 如何使用,平移前的坐标是如何指定的?(移动整个物体)x, y and z is the translation distances along the three axes.
- void glRotate{fd} (TYPE angle, TYPE x, TYPE y, TYPE z); 绕 vector(x,y,z) 旋转 angle 角度
- void glScale{fd}(TYPE Sx, TYPE Sy, TYPE Sz); Sx,Sy,Sz 分别为 x,y,z 变换的倍数
- Local transformation can be implemented by inverse the multiplying order of the global transformation :局部变换可以通过全局变换的逆乘法顺序实现(顺序完全颠倒即可)
- Global Transformation and Local Transformation
- Global transformation
- 每一次变换均可以看成是相对于原始坐标系执行的
- 后调用的变换矩阵乘在先前矩阵的左边
- 先调用的变换矩阵先执行
- Local transformation
- 每一次变换均可以看成是在上一次变换所形成的新的坐标系中进行
- 后调用的变换矩阵乘在先前矩阵的右边
- 后调用的变换矩阵先执行
- Global transformation
- 两个函数的使用方法:
- void glFrustum(GLdouble left, GLdouble right, GLdouble bottom, GLdouble top, GLdouble znear, GLdouble zfar );
- void gluPerspective(GLdouble fovy, GLdouble aspect, GLdouble zNear, GLdouble zFar);
- Z-buffer 算法: Z-Buffer 算法在像素级上以近物取代远物。面片在屏幕上的出现顺序是无关紧要的。